hasura/gitkube

Build and deploy docker images to Kubernetes using git push
| repo name | hasura/gitkube |
| repo link | https://github.com/hasura/gitkube |
| homepage | https://gitkube.sh |
| language | Go |
| size (curr.) | 37226 kB |
| stars (curr.) | 3111 |
| created | 2018-03-08 |
| license | Apache License 2.0 |

Gitkube
Gitkube is a tool for building and deploying Docker images on Kubernetes using git push.
After a simple initial setup, users can simply keep git push-ing their repos to build and deploy to Kubernetes automatically.
When should I use gitkube?
- Ideal for development where you can push your WIP branch to the cluster to test.
- Reference implementation for writing git-based automation on your server. Fork this repo and create your own CRD + controller + git remote hook that can do things on the Kubernetes cluster.
Features:
- No dependencies except native tooling (git, kubectl)
- Plug and play installation
- Simple public key based authentication
- RBAC ready - Control access to git remotes using RBAC
- Support for namespace based multi-tenancy - Remotes can only deploy to their own namespace
- No assumptions about repository structure
Getting started
Gitkube will run on any Kubernetes vendor/distribution AS IS. In case you find any difficulties in the setup, please comment on #33
Install gitkube
Using kubectl
kubectl create -f https://storage.googleapis.com/gitkube/gitkube-setup-stable.yaml
#expose gitkubed service
kubectl --namespace kube-system expose deployment gitkubed --type=LoadBalancer --name=gitkubed
Using gitkube CLI
-
Install Gitkube CLI:
- Linux/MacOS
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hasura/gitkube/master/gimme.sh | bash- Windows (using scoop)
scoop install gitkubeOr download the latest release and add it to your
PATH. -
Use Gitkube CLI to install Gitkube on the cluster:
gitkube install
Provider walkthroughs
The above installation steps work on most Kubernetes clusters. Detailed walkthroughs for few specific providers are also available:
| Provider | Link |
|---|---|
| minikube | minikube |
Example
Follow this example repo for a typical workflow of gitkube.
How it works
Gitkube has three components:
- Remote: Custom resource defined by a K8s CRD
- gitkube-controller: Controller that manages Remote objects and propogates changes to gitkubed
- gitkubed: Git host that builds docker image from the repo and rolls out deployment
High-level architecture
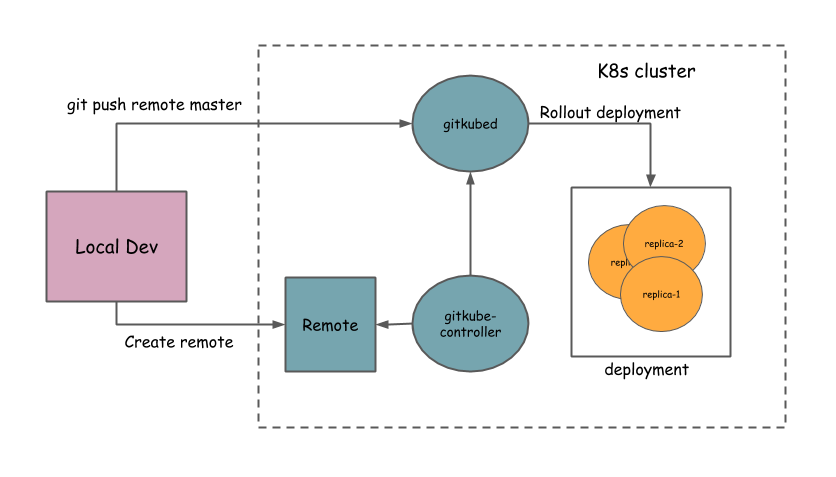
Workflow
- Local dev: User creates a base git repo for the application with Dockerfile and K8s deployment
- Setting Remote: User defines a spec for Remote containing the rules for
git push - Deploying application: Once a Remote is setup, application can be deployed to K8s using
git push <remote> master
Local dev
User should have a git repo with source code and a Dockerfile. User should also create a base K8s deployment for the application.
Setting Remote
A Remote resource consists of 3 parts:
- authorizedKeys: List of ssh-keys for authorizing
git push. - registry: Details of docker registry where images are pushed post-build.
- deployments: Spec for building docker image and updating corresponding K8s deployment.
Here is a typical spec for a Remote:
apiVersion: gitkube.sh/v1alpha1
kind: Remote
metadata:
name: sampleremote
namespace: default
spec:
# Insert ssh-keys for allowing users to git push
authorizedKeys:
- "ssh-rsa your-ssh-public-key"
# Provide registry details: https://github.com/hasura/gitkube/blob/master/docs/registry.md
registry:
url: "docker.io/user"
credentials:
secretRef: regsecret # Name of docker-registry secret
# Define deployment rules
deployments:
- name: www # Name of K8s deployment which is updated on git push
containers:
- name: www # Name of container in the deployment which is built during git push
path: example/www # Docker build context path in the git repo
dockerfile: example/www/Dockerfile # Location of Dockerfile for the source code
Deploying application
Once a Remote is created, it gets a git remote URL which you can find in its status spec
$ kubectl get remote sampleremote -o yaml
...
status:
remoteUrl: ssh://default-sampleremote@35.225.226.96/~/git/default-sampleremote
remoteUrlDesc: ""
Add the generated remoteUrl in git
$ git remote add sampleremote ssh://default-sampleremote@35.225.226.96/~/git/default-sampleremote
And finally, git push
$ git push sampleremote master
Roadmap
Gitkube is open to evolution. Some of the features to be added in future include:
- Allowing all apps (daemonset, statefulset) to be deployed using
git push. Current support is limited to deployments. #19 - Allowing different git hooks to be integrated #20
Contributing
Gitkube is an open source project licensed under Apache License 2.0
Contributions are welcome.
Community and Support
-
Join the Gitkube channel in the Kubernetes Slack group
Maintainers
This project has come out of the work at hasura.io. Current maintainers @Tirumarai, @shahidh_k.
Follow @gitkube to stay updated.
Gitkube logo concept and design by Samudra Gupta.





