neubig/lowresource-nlp-bootcamp-2020
The website for the CMU Language Technologies Institute low resource NLP bootcamp 2020
| repo name | neubig/lowresource-nlp-bootcamp-2020 |
| repo link | https://github.com/neubig/lowresource-nlp-bootcamp-2020 |
| homepage | |
| language | Jupyter Notebook |
| size (curr.) | 31489 kB |
| stars (curr.) | 163 |
| created | 2020-05-24 |
| license | BSD 3-Clause “New” or “Revised” License |
CMU LTI Low Resource NLP Bootcamp 2020
This is a page for a low-resource natural language and speech processing bootcamp held by the Carnegie Mellon University Language Technologies Institute in May 2020. The bootcamp was held virtually for some visitors to the institute, but we are making the videos and materials available for those interested in learning on your own. It comes in 8 parts, all with lecture videos and example exercises that you can do to expand your knowledge.
1. NLP Tasks
This lecture by Graham Neubig gives a high-level overview of a variety of NLP tasks (slides).
The exercise has participants download spaCy and see the types of linguistic outputs generated in its tutorial. We also examined the Universal Dependencies Treebank to see the various other languages that have annotated data such as that generated by spaCy’s analysis.
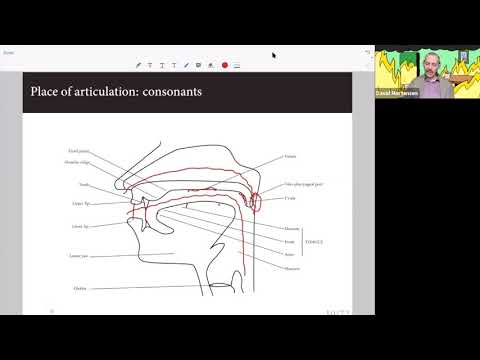
2. Linguistics - Phonology and Morphology
This lecture by David Mortensen gives some linguistic background of phonology and morphology (slides).
The exercise has participants use epitran to generate phonetic transcriptions of words, and try to read some words in the international phonetic alphabet.
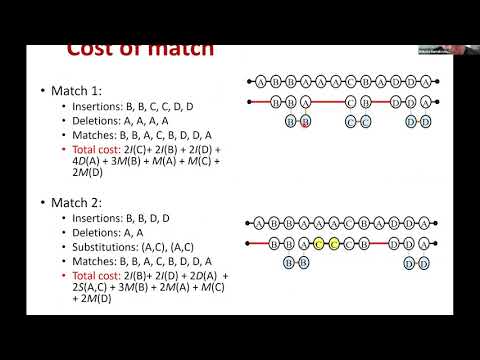
3. Machine Translation
This lecture by Antonis Anastasopoulos explains about machine translation, both phrase-based and neural (slides).
The exercise runs through tutorials on word alignment with fast-align, and neural machine translation with JoeyNMT using data from the Latvian-English translation task at WMT.
4. Linguistics - Syntax and Morphosyntax
This lecture by Lori Levin explains about aspects of linguistics related to syntax and morphosyntax (slides).
The exercise consists of creating an interlinear gloss for the language of your choice.
5. Neural Representation Learning
This lecture by Pengfei Liu explains about various methods for learning neural representations of language (slides).
The exercise, by Antonis Anastasopoulos, introduces learning of word representations using fastText, using them for simple text classification, and finding similar words.
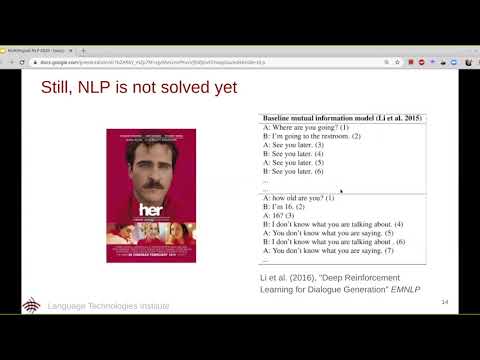
6. Multilingual NLP
This lecture by Yulia Tsvetkov explains about how you can train multilingual NLP systems that work in many different languages (slides).
The exercise, by Chan Park, provides two Jupyter noteboks that explain how to train a Naive Bayes Classifier for classification across languages, and introduces how to use multilingual BERT for cross-lingual classification.
7. Speech Synthesis
This lecture by Alan Black explains about speech synthesis, generating speech from text (slides: overview, building voices, unwritten languages).
The exercise demonstrates how you can build your own talking clock using your voice in a language of your choice, and you can get instructions here and here.
8. Speech Recognition
This lecture by Bhiksha Raj explains about speech recognition, converting speech into textual transcriptions (slides).
The exercise, by Hira Dhamyal, demonstrates how to build a speech recognition system in Kaldi, specifically focusing on the mini-librispeech example.