omerbsezer/Fast-Pytorch

Pytorch Tutorial, Pytorch with Google Colab, Pytorch Implementations: CNN, RNN, DCGAN, Transfer Learning, Chatbot, Pytorch Sample Codes
| repo name | omerbsezer/Fast-Pytorch |
| repo link | https://github.com/omerbsezer/Fast-Pytorch |
| homepage | |
| language | Jupyter Notebook |
| size (curr.) | 95790 kB |
| stars (curr.) | 280 |
| created | 2019-04-09 |
| license | |
Fast-Pytorch
This repo aims to cover Pytorch details, Pytorch example implementations, Pytorch sample codes, running Pytorch codes with Google Colab (with K80 GPU/CPU) in a nutshell.
Running in Colab
- Two way:
- Clone or download all repo, then upload your drive root file ('/drive/'), open .ipynb files with ‘Colaboratory’ application
- Download “Github2Drive.ipynb” and copy your drive root file, open with ‘Colaboratory’ and run 3 cells one by one, hence repo is cloned to your drive file. (Pytorch with Google Colab)
Table of Contents:
- :fire:Fast Pytorch Tutorial
- :fire:Fast Torchvision Tutorial
- :fire:Pytorch with Google Colab
- :fire:Pytorch Example Implementations
- MLP
- MLP 1 Class with Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) Loss: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- MLP 2 Classes with Cross Entropy Loss: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- MLP 3-Layer with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- CNN
- CNN with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- Improved CNN with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- CNN Visualization
- CNN Visualization: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- RNN
- RNN Text Generation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- Transfer Learning
- Transfer Learning Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- DCGAN
- DCGAN Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- ChatBot
- Chatbot Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- MLP
- :fire:Pytorch Sample Codes
Fast Pytorch Tutorial
It’s python deep learning framework/library that is developed by Facebook. Pytorch has own datastructure that provides automatic differentiation for all operations on Tensors.
- What is Pytorch?
- Autograd: Automatic Differentiation
- Details - Deep Learning with PyTorch: A 60 Minute Blitz
Important keys: torch.Tensor, .requires_grad, .backward(), .grad, with torch.no_grad().
Pytorch CheatSheet: :fire:Details
Pytorch Playground
- :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
Model (Neural Network Layers)
- :fire:Details
torch.nn.RNN(*args, **kwargs)
torch.nn.LSTM(*args, **kwargs)
torch.nn.GRU(*args, **kwargs)
torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size, hidden_size, bias=True, nonlinearity='tanh')
torch.nn.LSTMCell(input_size, hidden_size, bias=True)
torch.nn.GRUCell(input_size, hidden_size, bias=True)
torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)
torch.nn.Bilinear(in1_features, in2_features, out_features, bias=True)
torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
torch.nn.Conv3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
torch.nn.Unfold(kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
torch.nn.Fold(output_size, kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1)
Optimizer
- :fire:Details
torch.optim.Adadelta(params, lr=1.0, rho=0.9, eps=1e-06, weight_decay=0)
torch.optim.Adagrad(params, lr=0.01, lr_decay=0, weight_decay=0, initial_accumulator_value=0)
torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False)
torch.optim.SparseAdam(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08)
torch.optim.Adamax(params, lr=0.002, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0)
torch.optim.ASGD(params, lr=0.01, lambd=0.0001, alpha=0.75, t0=1000000.0, weight_decay=0)
torch.optim.LBFGS(params, lr=1, max_iter=20, max_eval=None, tolerance_grad=1e-05, tolerance_change=1e-09, history_size=100, line_search_fn=None)
torch.optim.RMSprop(params, lr=0.01, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False)
torch.optim.Rprop(params, lr=0.01, etas=(0.5, 1.2), step_sizes=(1e-06, 50))
torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=<required parameter>, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False) # stochastic gradient descent
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch=-1)
torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size, gamma=0.1, last_epoch=-1)
Loss Functions
- :fire:Details
torch.nn.L1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') # L1 Loss
torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') # Mean square error loss
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='mean') #Connectionist Temporal Classification loss
torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean') #negative log likelihood loss
torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=False, size_average=None, eps=1e-08, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
torch.nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') # Kullback-Leibler divergence Loss
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean') # Binary Cross Entropy
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
Pooling Layers
- :fire:Details
torch.nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False)
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False)
torch.nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False)
torch.nn.MaxUnpool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0) # Computes a partial inverse of MaxPool2d
torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True)
torch.nn.FractionalMaxPool2d(kernel_size, output_size=None, output_ratio=None, return_indices=False, _random_samples=None)
torch.nn.LPPool2d(norm_type, kernel_size, stride=None, ceil_mode=False) # 2D power-average pooling
torch.nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(output_size, return_indices=False)
torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size)
Non-linear activation functions
- :fire:Details
torch.nn.ELU(alpha=1.0, inplace=False) # the element-wise function
torch.nn.Hardshrink(lambd=0.5) # hard shrinkage function element-wise
torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)
torch.nn.PReLU(num_parameters=1, init=0.25)
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
torch.nn.RReLU(lower=0.125, upper=0.3333333333333333, inplace=False) # randomized leaky rectified liner unit function
torch.nn.SELU(inplace=False)
torch.nn.CELU(alpha=1.0, inplace=False)
torch.nn.Sigmoid()
torch.nn.Softplus(beta=1, threshold=20)
torch.nn.Softshrink(lambd=0.5)
torch.nn.Tanh()
torch.nn.Tanhshrink()
torch.nn.Threshold(threshold, value, inplace=False)
torch.nn.Softmax(dim=None)
torch.nn.Softmax2d()
Basic 2 Layer NN
- Basic two layer feed forward neural networks with optimizer, loss:
import torch
class TwoLayerNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, D_in, H, D_out):
super(TwoLayerNet, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(D_in, H)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(H, D_out)
def forward(self, x):
h_relu = self.linear1(x).clamp(min=0)
y_pred = self.linear2(h_relu)
return y_pred
N_batchsize, D_input, Hidden_size D_output = 64, 1000, 100, 10
epoch=500
x = torch.randn(N_batchsize, D_input)
y = torch.randn(N_batchsize, D_output)
model = TwoLayerNet(D_input, Hidden, D_output)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum') # loss, mean square error
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4) # optimizer, stochastic gradient descent, lr=learning rate
for t in range(epoch):
y_pred = model(x) # Forward pass
loss = criterion(y_pred, y) #print(t, loss.item())
optimizer.zero_grad() # Zero gradients,
loss.backward() # backward pass
optimizer.step() # update the weights
Fast Torchvision Tutorial
“The torchvision package consists of popular datasets, model architectures, and common image transformations for computer vision.”
ImageFolder
- If you have special/custom datasets, image folder function can be used.
# Example
imagenet_data = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder('path/to/imagenet_root/')
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(imagenet_data,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=args.nThreads)
Transforms
- Transforms are common for image transformations. :fire:Details
# Some of the important functions:
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((input_size, input_size)), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) 3 Example
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(size)
torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0)
torchvision.transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1)
torchvision.transforms.Pad(padding, fill=0, padding_mode='constant')
torchvision.transforms.RandomApply(transforms, p=0.5)
torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop(size, padding=None, pad_if_needed=False, fill=0, padding_mode='constant')
torchvision.transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.1)
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(size, scale=(0.08, 1.0), ratio=(0.75, 1.3333333333333333), interpolation=2)
torchvision.transforms.RandomRotation(degrees, resample=False, expand=False, center=None)
torchvision.transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5)
torchvision.transforms.Resize(size, interpolation=2)
torchvision.transforms.Scale(*args, **kwargs)
torchvision.transforms.LinearTransformation(transformation_matrix)
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean, std, inplace=False) # Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() # Convert a PIL Image or numpy.ndarray to tensor
# Functional transforms give you fine-grained control of the transformation pipeline. As opposed to the transformations above, functional transforms don’t contain a random number generator for their parameters. That means you have to specify/generate all parameters, but you can reuse the functional transform.
torchvision.transforms.functional.adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor)
torchvision.transforms.functional.hflip(img)
torchvision.transforms.functional.normalize(tensor, mean, std, inplace=False) # Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation
torchvision.transforms.functional.pad(img, padding, fill=0, padding_mode='constant')
torchvision.transforms.functional.rotate(img, angle, resample=False, expand=False, center=None) # Rotate the image by angle
torchvision.transforms.functional.to_grayscale(img, num_output_channels=1) # Convert image to grayscale version of image.
Datasets
- Most used datasets in the literature. :fire:Details
torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='data/mnist', train=True, transform=transform, target_transform=None, download=True) # with example
torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='data/fashion-mnist', train=True, transform=transform, target_transform=None, download=True) # with example
torchvision.datasets.KMNIST(root, train=True, transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)
torchvision.datasets.EMNIST(root, split, **kwargs)
torchvision.datasets.FakeData(size=1000, image_size=(3, 224, 224), num_classes=10, transform=None, target_transform=None, random_offset=0)
torchvision.datasets.CocoCaptions(root, annFile, transform=None, target_transform=None)
torchvision.datasets.CocoDetection(root, annFile, transform=None, target_transform=None)
torchvision.datasets.LSUN(root, classes='train', transform=None, target_transform=None)
torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root, train=True, transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)
torchvision.datasets.STL10(root, split='train', transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)
torchvision.datasets.SVHN(root, split='train', transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)
torchvision.datasets.PhotoTour(root, name, train=True, transform=None, download=False)
torchvision.datasets.SBU(root, transform=None, target_transform=None, download=True)
torchvision.datasets.Flickr8k(root, ann_file, transform=None, target_transform=None)
torchvision.datasets.VOCSegmentation(root, year='2012', image_set='train', download=False, transform=None, target_transform=None)
torchvision.datasets.Cityscapes(root, split='train', mode='fine', target_type='instance', transform=None, target_transform=None)
Models
- :fire:Details
# model with random weights
import torchvision.models as models
resnet18 = models.resnet18()
alexnet = models.alexnet()
vgg16 = models.vgg16()
squeezenet = models.squeezenet1_0()
densenet = models.densenet161()
inception = models.inception_v3()
googlenet = models.googlenet()
# with pre-trained models
resnet18 = models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
alexnet = models.alexnet(pretrained=True)
squeezenet = models.squeezenet1_0(pretrained=True)
vgg16 = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
densenet = models.densenet161(pretrained=True)
inception = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
googlenet = models.googlenet(pretrained=True)
Utils
torchvision.utils.make_grid(tensor, nrow=8, padding=2, normalize=False, range=None, scale_each=False, pad_value=0) # Make a grid of images.
torchvision.utils.save_image(tensor, filename, nrow=8, padding=2, normalize=False, range=None, scale_each=False, pad_value=0) # Save a given Tensor into an image file
Pytorch with Google Colab
- If you want to use drive.google for storage, you have to run the following codes for authentication. After running cell, links for authentication are appereared, click and copy the token pass for that session.
!apt-get install -y -qq software-properties-common python-software-properties module-init-tools
!add-apt-repository -y ppa:alessandro-strada/ppa 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get update -qq 2>&1 > /dev/null
!apt-get -y install -qq google-drive-ocamlfuse fuse
from google.colab import auth
auth.authenticate_user()
from oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials
creds = GoogleCredentials.get_application_default()
import getpass
!google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret} < /dev/null 2>&1 | grep URL
vcode = getpass.getpass()
!echo {vcode} | google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret}
- Then, you can use your drive file and reach the your codes which are in your drive.
!mkdir -p drive
!google-drive-ocamlfuse drive
import sys
sys.path.insert(0,'drive/Fast-Pytorch/Learning_Pytorch') # Example, your drive root: 'drive/'
!ls drive
- After authentication, git clone command is also used to clone project.
%cd 'drive/Fast-Pytorch'
!ls
!git clone https://github.com/omerbsezer/Fast-Pytorch.git
Pytorch Example Implementations
- All codes are run on the Colab. You can also run on desktop jupyter notebooks.(Anaconda)[https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/].
MLP
- MLP 1 Class with Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) Loss: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- MLP 2 Classes with Cross Entropy Loss: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- MLP 3-Layer with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model,self).__init__()
self.fc1 =torch.nn.Linear(x.shape[1],5)
self.fc2 =torch.nn.Linear(5,3)
self.fc3 =torch.nn.Linear(3,1)
self.sigmoid=torch.nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
out =self.fc1(x)
out =self.sigmoid(out)
out =self.fc2(out)
out =self.sigmoid(out)
out =self.fc3(out)
out= self.sigmoid(out)
return out
CNN
- CNN with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- Improved CNN with MNIST Example: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN,self).__init__()
# input_size:28, same_padding=(filter_size-1)/2, 3-1/2=1:padding
self.cnn1=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=8, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# input_size-filter_size +2(padding)/stride + 1 = 28-3+2(1)/1+1=28
self.batchnorm1=nn.BatchNorm2d(8)
# output_channel:8, batch(8)
self.relu=nn.ReLU()
self.maxpool1=nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
#input_size=28/2=14
self.cnn2=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=8, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
# same_padding: (5-1)/2=2:padding_size.
self.batchnorm2=nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.maxpool2=nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# input_size=14/2=7
# 32x7x7=1568
self.fc1 =nn.Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=600)
self.dropout= nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
self.fc2 =nn.Linear(in_features=600, out_features=10)
def forward(self,x):
out =self.cnn1(x)
out =self.batchnorm1(out)
out =self.relu(out)
out =self.maxpool1(out)
out =self.cnn2(out)
out =self.batchnorm2(out)
out =self.relu(out)
out =self.maxpool2(out)
out =out.view(-1,1568)
out =self.fc1(out)
out =self.relu(out)
out =self.dropout(out)
out =self.fc2(out)
return out
CNN Visualization
- CNN Visualization: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
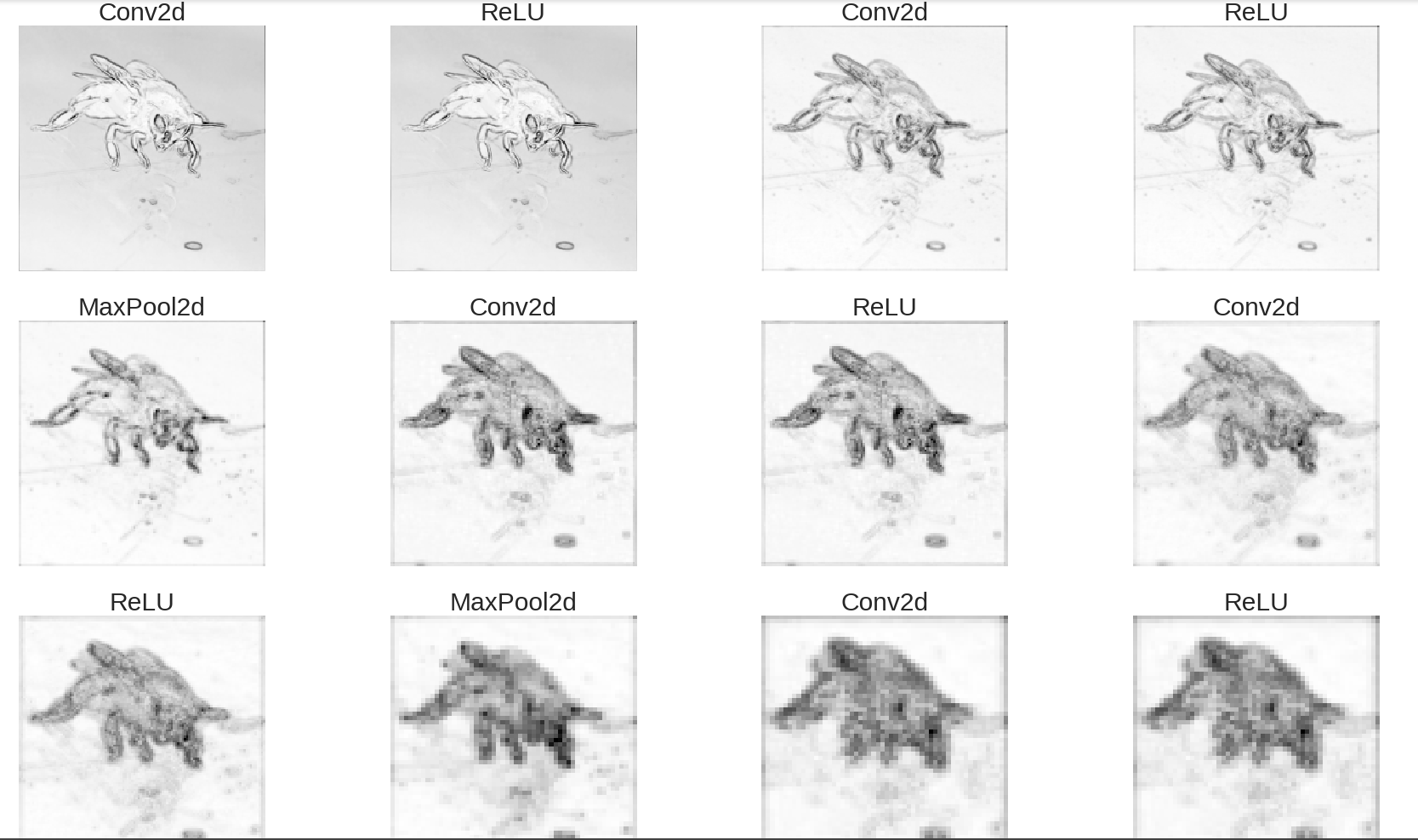
RNN
- RNN Text Generation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
class TextGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, hidden_size, num_layers):
super(TextGenerator, self).__init__()
self.embed= nn.Embedding(vocab_size,embed_size)
self.lstm=nn.LSTM(embed_size,hidden_size,num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.linear=nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size)
def forward(self,x,h):
x= self.embed(x)
# h: hidden_state, c=output
# x= x.view(batch_size,timesteps,embed_size)
out, (h,c)=self.lstm(x,h)
#(batch_size*timesteps, hidden_size)
#out.size(0):batch_size; out.size(1):timesteps, out.size(2): hidden_size
out=out.reshape(out.size(0)*out.size(1),out.size(2))
# decode hidden states of all time steps
out= self.linear(out)
return out, (h,c)
Transfer Learning
- Transfer Learning Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]

DCGAN
- DCGAN Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]

class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is Z, going into a convolution
nn.ConvTranspose2d( nz, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False), # input channel=100, o_channel:512, kernel=4, stride=1, padding=0
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf, nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# state size. (nc) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is (nc) x 64 x 64
nn.Conv2d(nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
ChatBot
- Chatbot Implementation: :green_book:[Colab], :notebook:[Notebook]
- Chatbot implementation details.
> what is your name?
Bot: berger .
> are you married?
Bot: no .
> how old are you?
Bot: i m not hungry .
> how are you?
Bot: okay .
> where are you from?
Bot: i m travelling .
> do you know me?
Bot: yes .
> who am i?
Bot: i don t know .
> what is your job?
Bot: i m not going to tell you .
> what is your problem?
Bot: i m not afraid of anything .
> are you robot?
Error: Encountered unknown word.
> what is my name?
Bot: berger .
> ai?
Error: Encountered unknown word.
> what do you want to me?
Bot: i m going to kill you .
> how do you kill me?
Bot: i told you .
> what is your plan?
Bot: i m not going to tell you .
> are you live?
Bot: yes .
> where?
Bot: the zoo .
> what is zoo?
Bot: the sheets . . .
> where is the zoo?
Bot: i don t know .
Pytorch Sample Codes
- CycleGAN [github], [github2]
- [Project] A simple PyTorch Implementation of Generative Adversarial Networks, focusing on anime face drawing, [github]
- Wiseodd/generative-models, both pytorch and tensorflow [github]
- GAN, LSGAN, WGAN, DRAGAN, CGAN, infoGAN, ACGAN, EBGAN, BEGAN [github]
- CartoonGAN github
- Pix2Pix [github]






